반응형
Spring boot에서 kafka 구축
Spring Boot를 이용하여 kafka API를 사용해보고자 한다.
사전조건
- kafka 설치 상태
- 개발도구 설치 상태
개발환경
- jdk : 1.8
- IDE : intelliJ
- build : gradle
- kafka 서버는 Ubuntu 18.04LTS에 설치되어 있다.
준비
- Producer를 통해 메시지를 보내고 Consumer를 통해 topic에 있는 데이터를 받아오는 프로그램을 간단하게 만들어보자.
| URL | 내용 |
|---|---|
| /send?msg= | Kafka source-topic에 메시지를 보낸다. |
| /receiver | Kafka source-topic에 들어간 메시지 한개 받는다. |
진행
1. zooKeeper, kafka 실행
Zookeeper실행
$ ./bin/kafka-zookeeper-server-start.sh config/zookeeper.propertiesKafka 실행
$ ./bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server.properties2. Kafka topic 생성
- source-topic을 생성한다.
$ ./bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --replication-factor 1 --partitions 1 --topic source-topic3. 구현
1. 프로젝트 생성
File -> module or project 선택
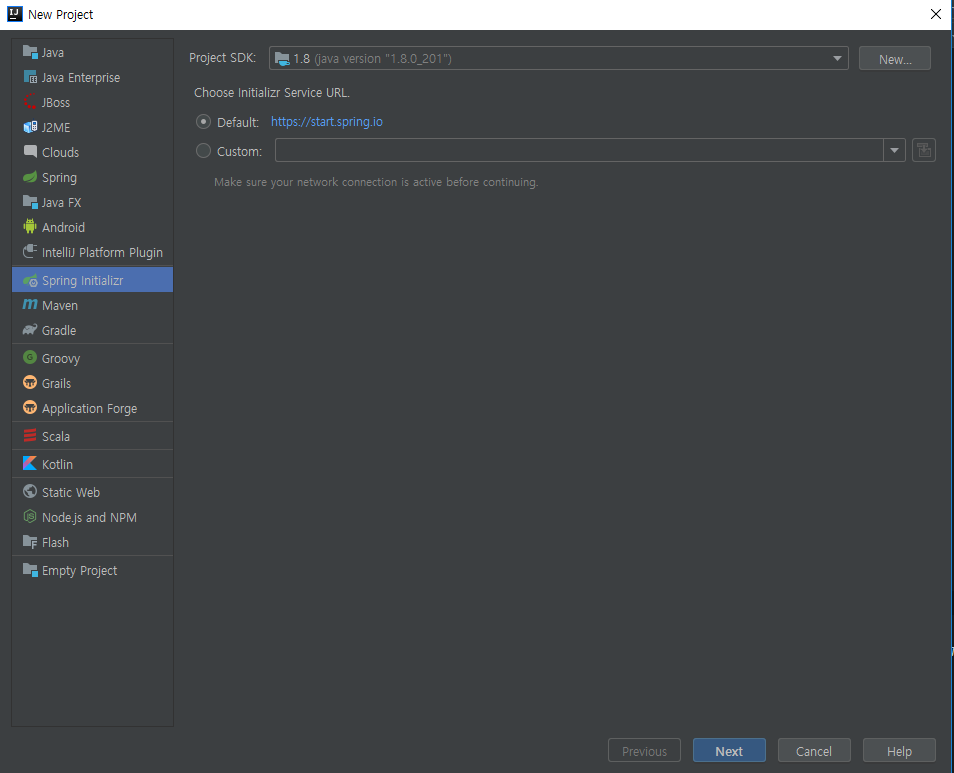
2. Prject Metadata 설정
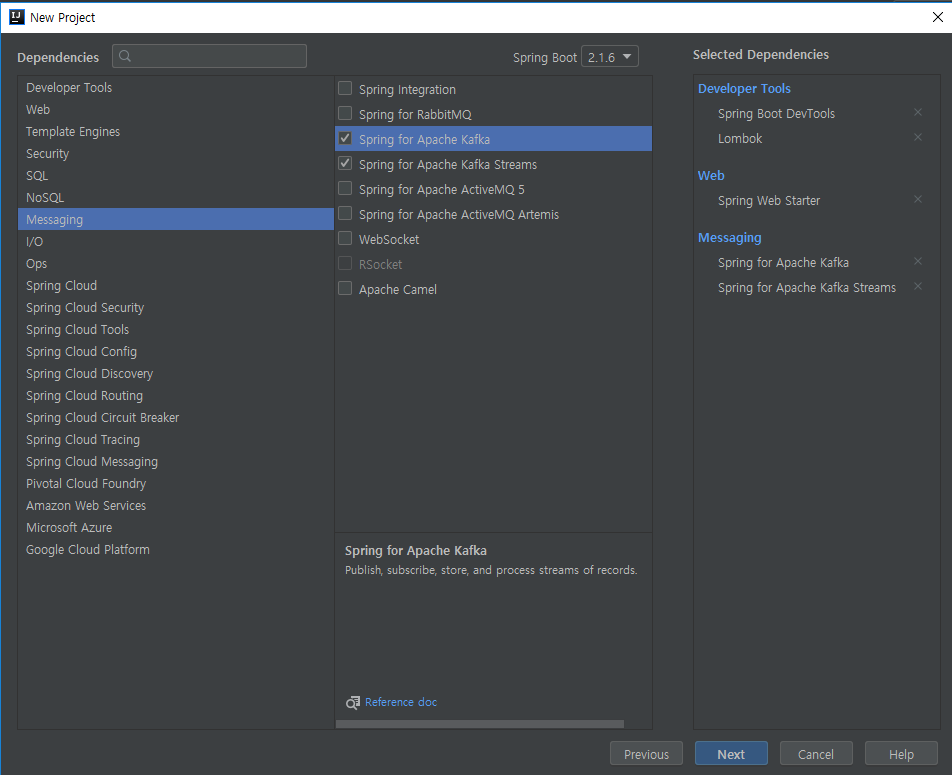
3. Dependencies 설정
- Web > Spring Web Starter 선택
- Developer Tools > Spring Boot DevTools, Lombok 선택
- Messaging > Spring for Apache kafka, Spring for ApacheKafka Streams 선택
4. 프로젝트 명 설정
5. Gradle 설정
6. kafka Producer, Consumer Properties 설정
- 스프링 부트 프로젝트를 생성하면 application.properties 가 생성되는데 application.properties는 지우고 application.yaml으로 바꿔서 사용했다.
아래와 같이 설정
[application.yaml]
## kafka Producer
spring:
kafka:
producer:
bootstrap-servers: localhost:9092
acks: all
key-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
value-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
batch-size: 1000
consumer:
bootstrap-servers: localhost:9092
key-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
value-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
group-id: SpringKafka
---
server:
port: 8096
---
kafka:
topic:
source-topic: source-topic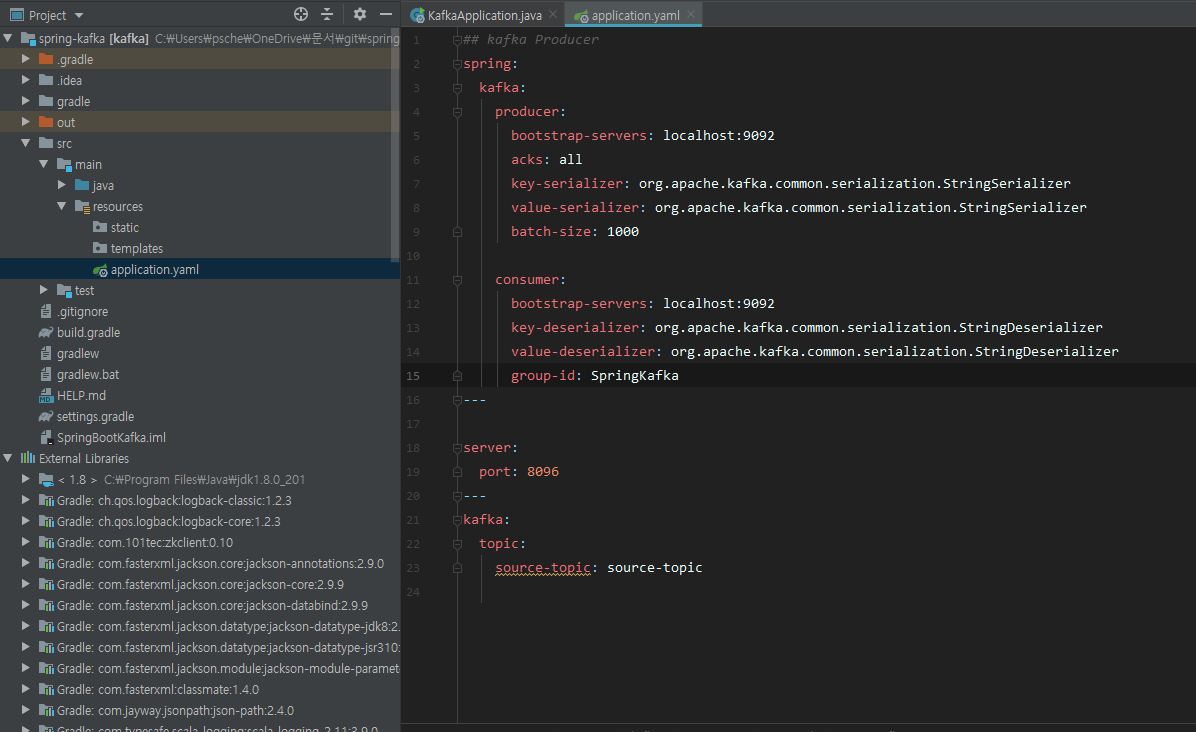
7. Producer, Consumer Config 설정
- @EnableKafka : Kafka를 사용할 수 있도록 자동으로 와이어링 해준다.
@EnableKafka
@Configuration
public class KafkaConfig {
}- Producer 설정
- producerProps()는 Producer를 실행하기위한 정보를 설정한다.
- ProducerFactory는 properties의 정보를 넣고 transaction을 설정할 수 있다.
- KafkaTemplate은 Kafka broker의 topic으로 데이터를 전송하도록 도와주는 역할을 한다.
@Bean
public Map<String, Object> producerProps() {
Map<String, Object> props = new HashMap<>();
props.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, env.getProperty("spring.kafka.producer.bootstrap-servers"));
props.put(ProducerConfig.ACKS_CONFIG, env.getProperty("spring.kafka.producer.acks"));
props.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, env.getProperty("spring.kafka.producer.key-serializer"));
props.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, env.getProperty("spring.kafka.producer.value-serializer"));
props.put(ProducerConfig.RETRIES_CONFIG, 0);
return props;
}
@Bean
public ProducerFactory<String, String> producerFactory() {
return new DefaultKafkaProducerFactory<String, String>(producerProps());
}
@Bean
public KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate() {
return new KafkaTemplate<>(producerFactory());
}- Consumer설정
- consumerProps()는 Consumer 환경설정 정보를 설정해준다.
- ConsumerFactory는 consumerProps()의 정보를 초기화를 해준다.
- KafkaListenerContainerFactory는 여러 개의 컨테이너를 만들 수 있고, 여러개의 factor를 구성할 수도 있다. ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer는 @KafkaListener 를 사용할 수 있게되고 해당 어노테이션을 통해 카프카 Consumer 데이터를 가져올 수 있다.
public Map<String, Object> consumerProps() {
Map<String, Object> props = new HashMap<>();
props.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, env.getProperty("spring.kafka.consumer.bootstrap-servers"));
props.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, env.getProperty("spring.kafka.consumer.key-deserializer"));
props.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, env.getProperty("spring.kafka.consumer.value-deserializer"));
props.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, env.getProperty("spring.kafka.consumer.group-id"));
return props;
}
@Bean
public ConsumerFactory<Integer, String> consumerFactory() {
return new DefaultKafkaConsumerFactory<>(consumerProps());
}
@Bean
KafkaListenerContainerFactory<ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer<Integer, String>> kafkaListenerContainerFactory() {
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<Integer, String> factory = new ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<>();
factory.setConsumerFactory(consumerFactory());
factory.setConcurrency(3);
factory.getContainerProperties().setPollTimeout(3000);
return factory;
}[KafkaConfig.java]
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerConfig;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerConfig;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.EnableKafka;
import org.springframework.kafka.config.ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory;
import org.springframework.kafka.config.KafkaListenerContainerFactory;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.*;
import org.springframework.kafka.listener.ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@EnableKafka
@Configuration
public class KafkaConfig {
private Environment env;
@Autowired
public KafkaConfig(Environment env) {
this.env = env;
}
/**
* Producer Properties
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Map<String, Object> producerProps() {
Map<String, Object> props = new HashMap<>();
props.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, env.getProperty("spring.kafka.producer.bootstrap-servers"));
props.put(ProducerConfig.ACKS_CONFIG, env.getProperty("spring.kafka.producer.acks"));
props.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, env.getProperty("spring.kafka.producer.key-serializer"));
props.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, env.getProperty("spring.kafka.producer.value-serializer"));
props.put(ProducerConfig.RETRIES_CONFIG, 0);
return props;
}
/**
* Producer Factory
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public ProducerFactory<String, String> producerFactory() {
return new DefaultKafkaProducerFactory<String, String>(producerProps());
}
/**
* KafkaTemplate는 kafka broker의 topic으로 데이터를 전송하도록 도와주는 역할을 한다.
*
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate() {
return new KafkaTemplate<>(producerFactory());
}
/**
* Consumer Properties
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Map<String, Object> consumerProps() {
Map<String, Object> props = new HashMap<>();
props.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, env.getProperty("spring.kafka.consumer.bootstrap-servers"));
props.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, env.getProperty("spring.kafka.consumer.key-deserializer"));
props.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, env.getProperty("spring.kafka.consumer.value-deserializer"));
props.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, env.getProperty("spring.kafka.consumer.group-id"));
return props;
}
/**
* Consumer Factory
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public ConsumerFactory<Integer, String> consumerFactory() {
return new DefaultKafkaConsumerFactory<>(consumerProps());
}
/**
* Consumer Container factory
*ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory는
* @return
*/
@Bean
KafkaListenerContainerFactory<ConcurrentMessageListenerContainer<Integer, String>> kafkaListenerContainerFactory() {
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<Integer, String> factory = new ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<>();
factory.setConsumerFactory(consumerFactory());
factory.setConcurrency(3);
factory.getContainerProperties().setPollTimeout(3000);
return factory;
}
}8. Producer 구현
- Producer는 KafkaTemplate를 통해 메시지를 해당 Topic에게 전송할 수 있다.
kafkaTemplate.send(topic, message); 이 Kafka 서버로 해당 Topic으로 데이터를 전송하는 역할을 하고 ListenableFuture를 통해 Collback을 받을 수 있다.
ListenableFuture<SendResult<String, String>> future = kafkaTemplate.send(topic, message);
future.addCallback(new ListenableFutureCallback<SendResult<String, String>>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(SendResult<String, String> result) {
log.info("Send Message : [{}] with offset=[{}]", message, result.getRecordMetadata().offset());
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable ex) {
log.info("fail Message : {}, Exception : {}", message, ex.getMessage());
}
});[ProducerService.java]
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
import org.springframework.kafka.support.SendResult;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFuture;
import org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFutureCallback;
@Slf4j
@Service
public class ProducerService {
private final KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate;
@Autowired
public ProducerService(KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate) {
this.kafkaTemplate = kafkaTemplate;
}
@Value("${kafka.topic.source-topic}")
private String topic;
public void send(String message) {
log.info("Send Producer message : {}, topic={}", message, topic);
ListenableFuture<SendResult<String, String>> future = kafkaTemplate.send(topic, message);
future.addCallback(new ListenableFutureCallback<SendResult<String, String>>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(SendResult<String, String> result) {
log.info("Send Message : [{}] with offset=[{}]", message, result.getRecordMetadata().offset());
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable ex) {
log.info("fail Message : {}, Exception : {}", message, ex.getMessage());
}
});
}
}9. Consumer 구현
- @KafkaListener 어노테이션을 통해 Consumer 정보를 받을 수 있다. 원래는 KafkaConsumer 객체를 통해 topic을 구독하고 consumer.poll() 을통해 topic정보를 Polling 했지만, Spring Kafka에서는 @KafkaListener를 통해 이 역할을 수행한다.
- @KafkaListener 의 상세정보를 보려면 Spring for Apache Kafka reference를 참조
기존 Kafka API호출
private final KafkaConsumer<String, String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer<String, String>(Consumer.createConfig(servers, groupId));
public ConsumerRecords<String, String> consume() {
this.consumer.subscribe(Collections.singleton(this.topic)); //2. topic publish
return consumer.poll(Duration.ofMillis(100)); //3. set timeout
}Spring-Kafka API를 사용할 경우
[ConsumerService.java]
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.KafkaListener;
import org.springframework.messaging.MessageHeaders;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Headers;
import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.Payload;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Slf4j
@Data
@Service
public class ConsumerService {
private String LastMsg;
@KafkaListener(topics = "${kafka.topic.source-topic}")
public void receiver(@Payload String message, @Headers MessageHeaders headers) {
headers.keySet().forEach(key -> log.info("key={}, value={}", key, headers.get(key)));
log.info("Received Message : {}", message);
setLastMsg(message);
}
}10. Controller 구현
import com.springkafka.kafka.service.ConsumerService;
import com.springkafka.kafka.service.ProducerService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class KafkaController {
private final ProducerService producerService;
private final ConsumerService consumerService;
@Autowired
public KafkaController(ProducerService producerService, ConsumerService consumerService) {
this.producerService = producerService;
this.consumerService = consumerService;
}
@GetMapping("/send")
public String sendProducer(@RequestParam(value = "msg") String message) {
producerService.send(message);
return "success";
}
@GetMapping("/receiver")
public String getMsg() {
return consumerService.getLastMsg();
}
}11. build
- 오른쪽 창에서 gradle -> Tasks -> build 에서 clean을 한 후 build를 수행한다.
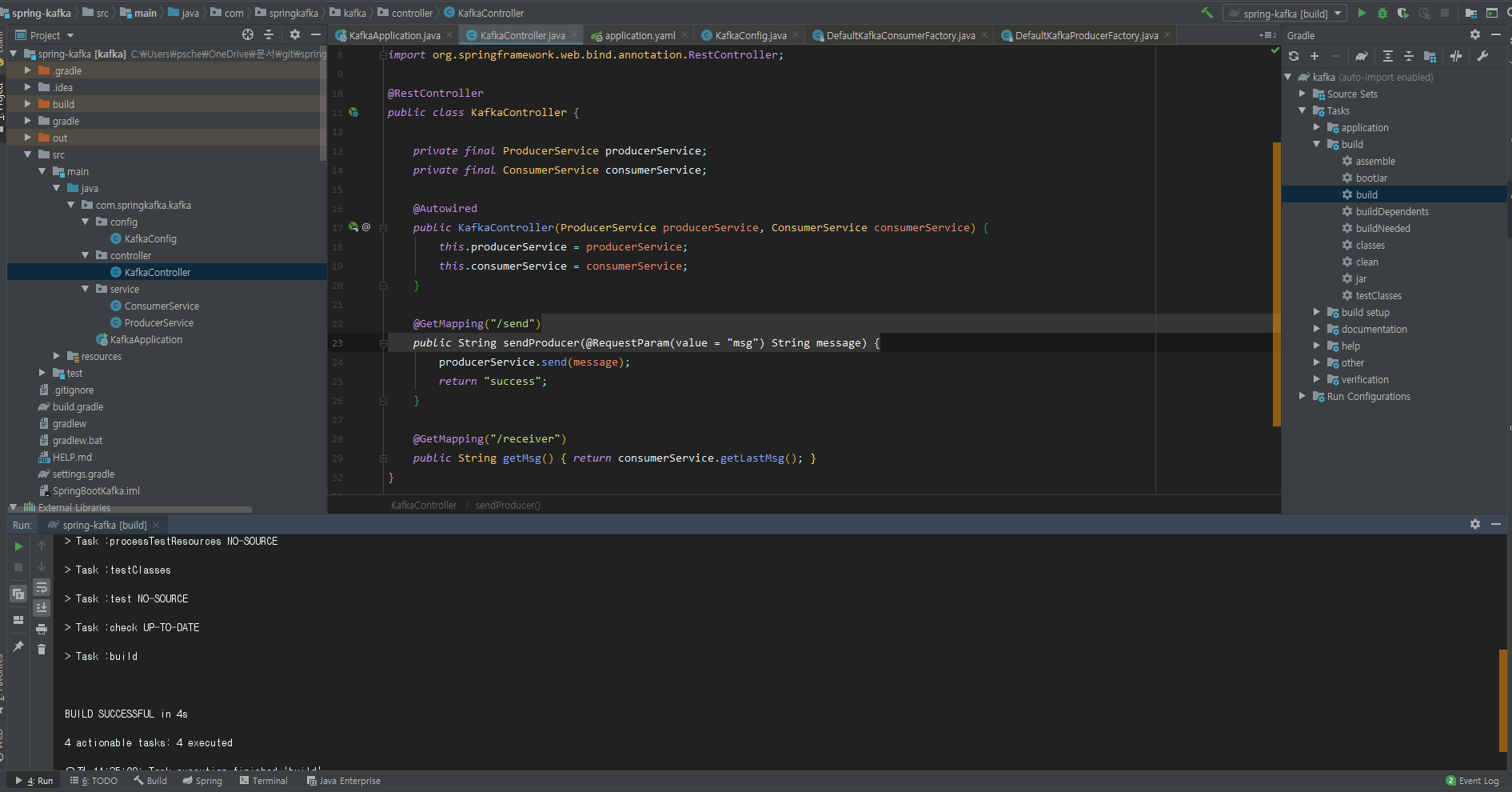
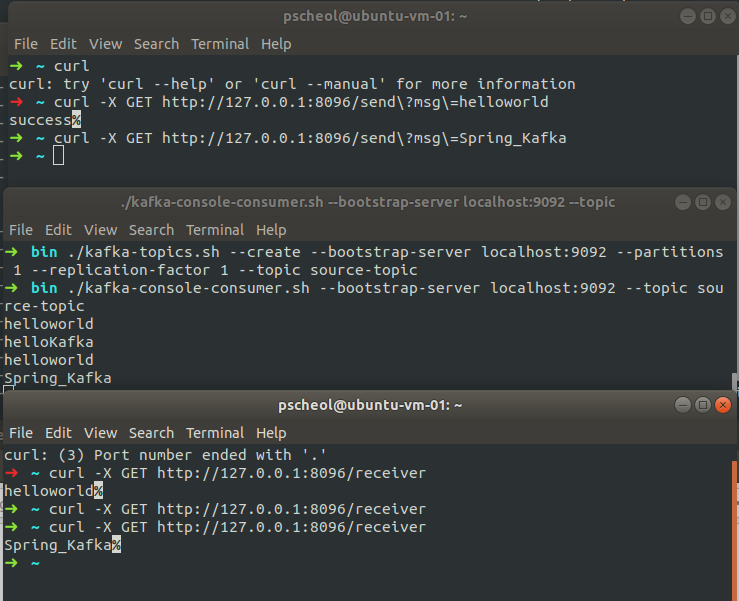
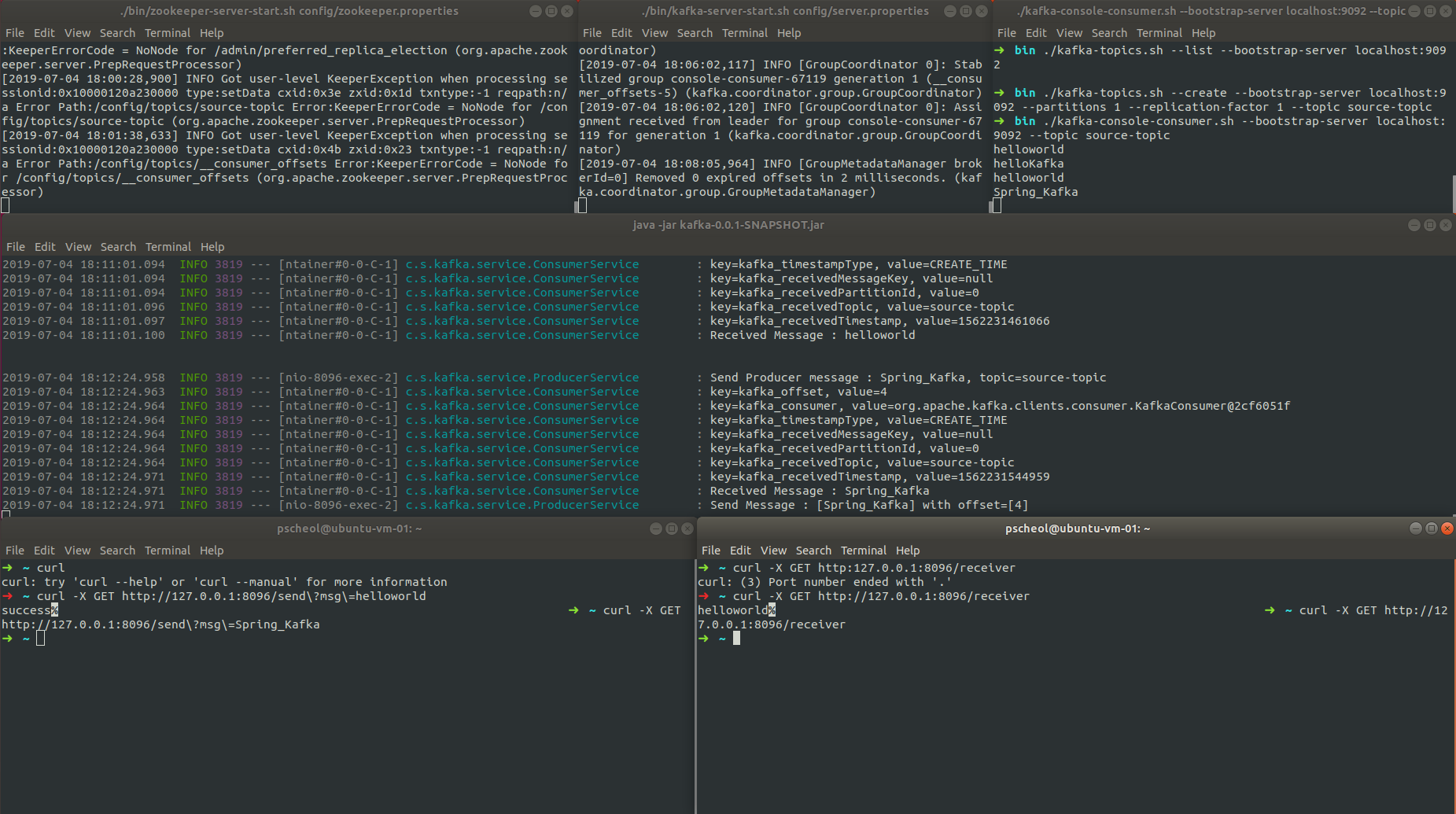
12. 실행 결과
- build 한 jar파일 실행(war를 만들었으면 톰캣에서 실행하면된다. Spring Boot Web을 선택했기에 내장 톰캣이 있어서 jar로 도 실행가능)
### .java -jar 파일명.jar
java -jar spring-kafka.jar[spring-kafka.jar 실행]

- kafka-console-consumer.sh를 실행하여 topic 데이터가 잘들어오는지 확인해보자
$ ./bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic source-topic- curl을 통해 테스트 수행
## /send?msg 요청 $ curl -X GET http://127.0.0.1:8096/send?msg=helloworld ## /receiver 요청 $ curl -X GET http://127.0.0.1:8096/receiver
참조 사이트
반응형
'Back-End > Kafka' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Kafka] 7. Apache Flume (0) | 2023.04.25 |
|---|---|
| [Kafka] 6.Kafka Streams (0) | 2023.04.25 |
| [Kafka] 5. kafka topic message 처리하기 (0) | 2023.04.25 |
| [Kakfka] 4. Kafka clusters (0) | 2023.04.24 |
| [Kakfa] 3. Kafka Producer & Consumer API (0) | 2023.04.24 |